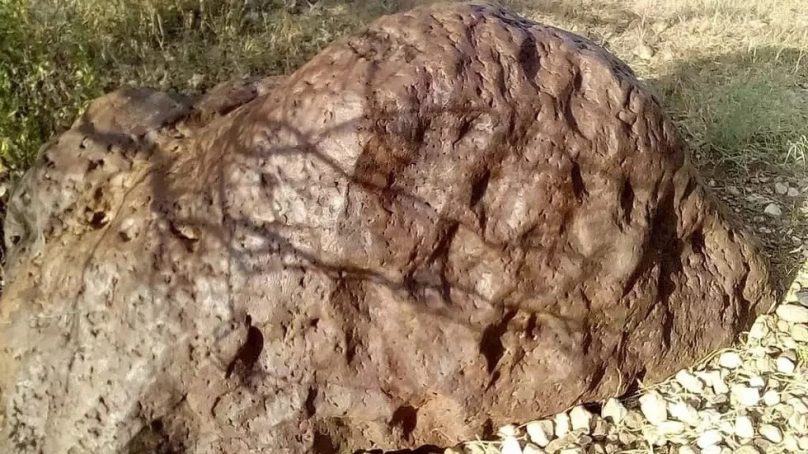
Scientists have identified two minerals never before seen on Earth in a meteorite weighing 15.2 metric tonnes (33,510 pounds).
The minerals came from a 70-gram (nearly 2.5-ounce) slice of the meteorite, which was discovered in Somalia in 2020 and is the ninth-largest meteorite ever found, according to a news release from the University of Alberta.
Chris Herd, curator of the university’s meteorite collection, received samples of the space rock so he could classify it. As he was examining it, something unusual caught his eye – some parts of the sample weren’t identifiable by a microscope. He then sought advice from Andrew Locock, head of the university’s Electron Microprobe Laboratory, because Locock has experience describing new minerals.
“The very first day he did some analyses, he said, “You’ve got at least two new minerals in there,’” Herd, a professor in the university’s department of Earth and atmospheric sciences, said in a statement. “That was phenomenal. Most of the time it takes a lot more work than that to say there’s a new mineral.”
One mineral’s name – elaliite – derives from the space object itself, which is called the “El Ali” meteorite since it was found near the town of El Ali in central Somalia.
Herd named the second one elkinstantonite after Lindy Elkins-Tanton, vice president of Arizona State University’s Interplanetary Initiative. Elkins-Tanton is also a regents professor in that university’s School of Earth and Space Exploration and the principal investigator of NASA’s upcoming Psyche mission – a journey to a metal-rich asteroid orbiting the sun between Mars and Jupiter, according to the space agency.
“Lindy has done a lot of work on how the cores of planets form, how these iron nickel cores form, and the closest analogue we have are iron meteorites,” Herd said. “It made sense to name a mineral after her and recognize her contributions to science.”
The International Mineralogical Association’s approval of the two new minerals in November of this year “indicates that the work is robust,” said Oliver Tschauner, a mineralogist and professor of research in the department of geoscience at the University of Nevada, Las Vegas.
- A Tell report