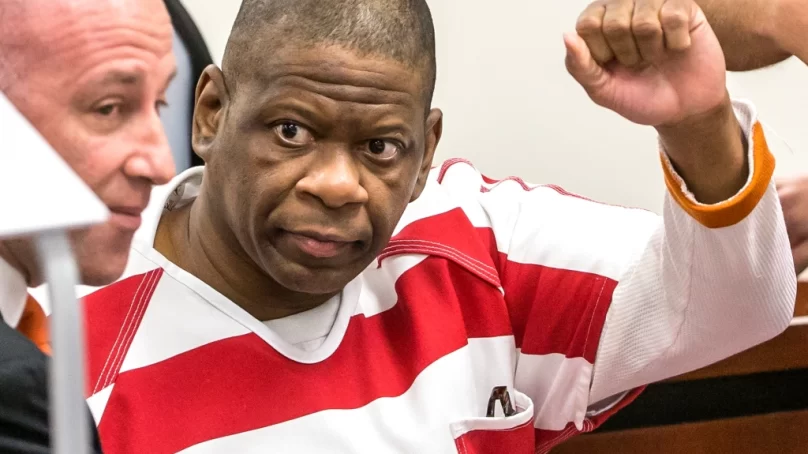
Despite overwhelming testimony in favour of Rodney Reed in a case he is accused of raping and murdering a white woman, Stacey Stites, the judge presiding over the evidentiary hearing fully embraced the state’s position that none of Reed’s witnesses were credible.
Judge J.D. Langley signed off on findings written by the state, concluding that only the state’s witnesses, including a white police officer named Jimmy Fennell, were reliable.
Reed’s attorneys challenged the ruling before the Texas Court of Appeal (CCA), arguing that Langley had abdicated his responsibility to make independent determinations about witness credibility by simply adopting the state’s proposed conclusions, which were rife with errors and factual misrepresentations about various testimony, including Hugen’s.
In one of the rulings released on June 28, nearly two years after the evidentiary hearing concluded, the CCA lamented the errors – it listed several in a footnote with the caveat that the list was “by no means exhaustive” – before undertaking its own assessment of the witnesses’ credibility.
Ultimately, the CCA concluded, as Langley had, that none of Reed’s witnesses were credible, save for one man whose father lived in the apartment just below Stites and Fennell, who reported hearing violent arguing on multiple occasions.
The man, Brent Sappington, said that he and his father, Bill, who has since died, approached a prosecutor the family knew at church to report what they’d heard. According to Sappington, the prosecutor, a man named Ted Weems, told them to hush up because investigators already had their suspect. Weems testified that Bill had reported the fighting upstairs, but he denied discouraging the family from coming forward. The CCA credited Sappington only to the extent that Weems “corroborated” his account; where the stories diverged, the CCA concluded that Weems was the one telling the truth. Sappington explained that he was initially hesitant to come forward because Fennell was in law enforcement and he feared his story would be dismissed, an explanation the court found to be an excuse that “strains credulity.”
Several other witnesses provided similar reasoning, saying they didn’t come forward sooner because they feared retaliation from a law enforcement community that they expected would protect its own. The court repeatedly found this explanation unconvincing.
Other witnesses, who said they didn’t realise that what they knew was important, were dismissed as likely fabricating their recollections. While it’s true that memory can be tricky, the CCA failed to engage with any nuance and instead deployed a false-memory blanket across multiple witness statements as a one-stop discrediting device.
“For 23 years, Texas illegally hid evidence that could have exonerated Rodney Reed.”
Where Hugen was concerned, the court stated that the account she offered was “unremarkable, even mundane.” The judges also took aim at her recollection about seeing bruises on Stites’s arms, concluding that jurors would not have believed that since no bruises were found on Stites’s arms during the autopsy.
As for the state’s alleged Brady violation, the CCA concluded that the information Hugen had was “immaterial” since one witness had previously testified at Reed’s trial that she’d seen Reed and Stites together at the grocery store. Hugen’s account wouldn’t have added anything, the judges wrote, despite the fact that Hugen had no connection to the Reed family, and had her information been disclosed in a timely way, it would have offered Reed’s defence another avenue of investigation.
The court took the position that other witness statements were immaterial because the state had deemed them dead leads. In other words, if Texas prosecutors decided that the statements were meaningless, then they had no obligation to turn them over – a bastardisation of Brady’s disclosure requirement that would afford prosecutors total discretion over what evidence is released to the defence.
Although prosecutors cited their Brady obligation in releasing the witness information to Reed’s attorneys in 2021, the CCA’s opinion seemed to endorse the notion that it would have been perfectly fine for them to leave the information forever buried in the state’s files.
That the CCA would rule against Reed is neither new nor surprising – nor is the judges playing mental gymnastics with legal standards to get them to their desired result.
For decades, the court has been a myopic, hegemonic institution, composed largely of middle-aged, white, male jurists who were former prosecutors – a mix of factors that has created an insulated worldview within the court’s chambers in Austin.
When the current presiding judge, Sharon Keller, first ran for a seat on the court back in 1994, she described herself as “pro-prosecutor,” meaning, she told a reporter, “seeing legal issues from the perspective of the state instead of the perspective of the defence.” That view has dominated the CCA bench for the past 30 years and reflects its approach to the Reed case.
The judge who wrote the June 28 opinions was its newest member, Jesse McClure, a former prosecutor-turned-Houston district court judge who was appointed to the bench in December 2020 by Texas Governor Greg Abbott.
Notably, he is only the third Black CCA judge since the court’s establishment in 1891. One judge, Scott Walker, dissented from the rulings but did not explain why.
Reed’s lawyers are frustrated. “For 23 years, Texas illegally hid evidence that could have exonerated Rodney Reed. He is an innocent man,” Jane Pucher, a senior staff attorney with the Innocence Project, said in a statement. “Texans should be outraged that prosecutorial misconduct is going unchecked, and the state is being given a license to cheat – even if it means sending an innocent man to his death.”
Pucher said Reed’s legal team is considering all its options, including asking the US Supreme Court to review the case.
Meanwhile, a separate legal effort to obtain DNA testing on key crime scene evidence, including lengths of the braided belt used to strangle Stites, is ongoing. Texas has long fought Reed’s bid to have the evidence tested; predictably, the CCA sided with the state, offering a novel interpretation of Texas’s DNA testing law to block Reed’s access. The dispute made it to the Supreme Court on a technical point, and this spring, the court ruled in Reed’s favour, sending the case back to the 5th US Circuit Court of Appeals.
Rodrick is frustrated by the CCA’s continued hostility toward his brother, but he has vowed to keep fighting. At the vigil in Washington DC, he recalled something that his mother, Sandra, told the court back in 1998 when Reed was convicted. “She said, ‘You may try to take my son’s life, but I guarantee you the whole world will know about it.’”
- The Intercept report