Uganda has for the third year running emerged as the top performer in Africa’s Electricity Regulatory Index Report published by the African Development Bank.
The East African country, along with Namibia, Tanzania, Zambia and Kenya, the other top performers, have regulators with the authority to exert the necessary oversight on the sector.
However, the overall electricity regulatory frameworks of African countries are poorly developed and most countries experience major regulatory weaknesses.
The ERI, a flagship report of the African Development Bank, is a composite index that measures the level of development of electricity sector regulatory frameworks in African countries against international standards and best practice.
“The African Development Bank has been at the forefront of efforts to mainstream electricity sector regulation issues in Africa within the broader sector discourse, recognizing the importance of establishing robust legal and regulatory frameworks to support the financial sustainability of the sector and attract private sector investment,” said Vice President Kevin Kariuki, Power, Energy, Climate and Green Growth, at the African Development Bank.
The third edition of the ERI report was launched during the Digital Energy Festival of the Africa Energy Forum, on November 5 2020. The event brought together more than 70 stakeholders in the energy sector, regulators, international organisations, and development finance institutions like Africa50 and the World Bank.
Director for Energy Financial Solutions Policy and Regulations at the African Development Bank Wale Shonibare said Covid-19-related restrictions had increased residential electricity demand and decreased industrial/commercial demand. This had resulted in shortfalls in the projected revenues of utilities.
“To address these challenges, regulators will be required to play an even more critical and central role post-Covid to ensure that the sector recovers with minimal and controlled impact on consumers and utilities,” Mr Shonibare said.
Director of Project Development at Africa50 Koffi Klousseh praised the ERI as a great tool for assessing the readiness of the electricity sector for private sector investments.
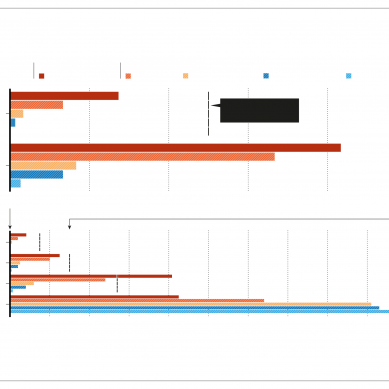
Main findings were:
• 69 per cent of countries surveyed have regulatory mechanisms in place to facilitate electricity access.
• In 21 of the 36 countries surveyed, the utility is not involved in funding rural electrification. The government, non-governmental organisations and consumers do this.
• In 90 per cent of the countries surveyed, the Executive holds the power to appoint board members and heads of regulatory institutions who report to them. This removes the core of decision-making independence from regulators, who are subjected to subtle and direct political pressure to skew key regulatory decisions towards the political inclination of the government in power.
• Most countries have legislation to deal with conflict of interest among commissioners and heads of regulatory institutions while in office. However, few have adequate mechanisms to regulate conflict of interest and other ethical issues, affecting the integrity of regulatory decisions.
• Political authorities have significant influence on the finances of regulatory authorities. In many instances, laws establishing regulatory institutions do not clearly indicate sources of funds for the institution.
- A Tell / APO Group report