Exposure to loud noise has long been linked with hearing loss. But the ruckus of planes and cars takes a toll beyond the ears. Traffic noise has been flagged as a major physiological stressor, second to air pollution and on roughly equal footing with exposure to second-hand smoke and radon.
In the last decade, a growing body of research more directly links air and road traffic noise to a heightened risk for a number of cardiovascular ailments – and scientists are beginning to pinpoint the mechanisms at play.
Evidence of noise’s physiological effects – whether on cells and organs or entire populations – “is really coming together and painting a picture of the problem,” says Mathias Basner, a psychiatrist and epidemiologist at the University of Pennsylvania and president of the International Commission on the Biological Effects of Noise.
Yet, he adds, few people are aware of the severity of what his colleagues refer to as a “silent killer.”
Graphic of a flow chart illustrating the effects of traffic noise on cardiovascular health. The downstream effects of stress hormones include the generation of damaging reactive oxygen species and inflammation within blood vessels, which can promote several cardiovascular problems.
Traffic noise can be annoying and stressful, triggering the release of stress hormones including cortisol, adrenaline and angiotensin II (ANGII). This stress reaction, especially when chronic, results in altered blood chemistry and meddles with blood vessel function.
An uptick in the number of damaging oxidants and proteins called adhesion molecules can remodel or ‘activate,’ the interior lining of blood vessels, the endothelium. This activity and the accompanying inflammation can lead to or exacerbate a number of cardiovascular problems.
Estimates suggest that roughly a third of Europeans and Americans are regularly exposed to unhealthy levels of noise, typically defined as starting around 70 to 80 decibels. For comparison, normal conversation is typically about 60 dB, cars and trucks range around 70 to 90 dB and sirens and airplanes can reach 120 dB or more.
Numerous studies link chronic exposure to such environmental noise to an increased risk of heart-related troubles. People living near the Frankfurt Airport, for example, have as much as a seven per cent higher risk of stroke than those living in similar but quieter neighbourhoods, according to a 2018 study in Noise&Health that investigated health data of more than one million people.
An analysis of nearly 25,000 cardiovascular deaths between 2000 and 2015 among people living near Switzerland’s Zurich Airport saw significant increases in night-time mortality after airplane flyovers, especially among women, a team reported last year in the European Heart Journal.
As researchers probe the physiology underlying noise’s cardiovascular consequences, they are zeroing in on a culprit: dramatic changes to the endothelium, the inner lining of arteries and blood vessels. This lining can go from a healthy state to one that’s “activated,” and inflamed, with potentially serious ramifications.
The path from noise to blood vessels goes something like this: When sound reaches the brain, it activates two important regions – the auditory cortex, which interprets noise and the amygdala, which manages emotional responses to it. As noise gets louder, and especially during sleep, the amygdala activates the body’s flight-or-fight response – even if the person is not aware of it.
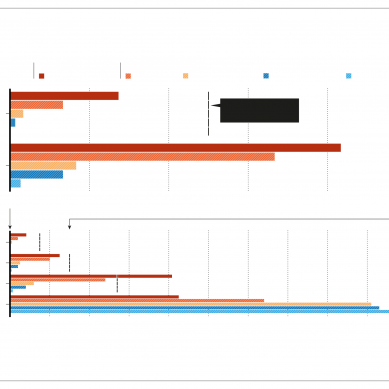
Five graphs illustrate the link between noise exposure and cardiovascular-related deaths, including heart failure, myocardial infarction and arrhythmias.
To probe how night-time noise affects health, researchers looked at death data from adults living near the Zurich airport from 2000 to 2015. People exposed to loud air traffic noise in the two hours before they died had a greater chance of dying from a heart attack (myocardial infarction), heart failure or arrhythmia (especially in women).
Once initiated, this stress response releases hormones such as adrenaline and cortisol into the body: Some arteries constrict, others dilate, blood pressure rises, digestion slows and sugars and fats flood the bloodstream for quick use by the muscles. The response may be enhanced if the noise is annoying or outside of a person’s control.
The cascading stress response also prompts the creation of harmful molecules that cause oxidative stress and inflammation in the lining of blood vessels. This dysfunctional endothelium meddles with blood flow and affects numerous other processes that, when impaired, contribute to a range of cardiovascular illnesses, including high blood pressure, plaque build-up in the arteries, obesity and diabetes.
Studies on people and mice show that the endothelium doesn’t work as well after just a few days of night-time airplane noise exposure, suggesting that loud noise isn’t a concern only for people already at risk for heart and metabolic problems.
Healthy adults subjected to train recordings during their slumber had impaired blood vessel function almost immediately, according to a 2019 study published by Münzel and his colleagues in Basic Research in Cardiology.
“We were surprised that young people, after hearing these sounds for just one night, had endothelial dysfunction,” says Münzel, co-author of an overview on noise and cardiovascular health in the 2020 Annual Review of Public Health. “We always thought this was something that takes years to develop.”
While the data continue to accumulate, untangling cause and effect can be tricky. It’s not easy to conduct long-term sleep experiments or to distinguish between the effects of daytime and night-time noise, or effects of the noise itself versus the combined effects of noise and air pollution (which often go hand-in-hand).
The consequences of environmental noise are also tough to parse due to the subjective nature of sound, says Andreas Xyrichis, a health services scientist at King’s College in London. Xyrichis studies hospital intensive care units, where ringing telephones and clattering food dishes can be comforting or counteractive to recovery, depending on the patient.
“We are really trying to make this distinction between decibel levels and perception of noise,” he says.
But despite the remaining questions, there is a growing recognition of the connections between noise pollution and reduced physical health. A 2018 report by the World Health Organization noted that each year, western Europeans are collectively losing more than 1.6 million years of healthy life because of traffic noise. This calculation is based on the number of premature deaths caused directly by noise exposure as well as the years lived with noise-induced disability or illness.
And that number is likely to grow. In 2018, 55 percent of people lived in cities, and by 2050 that count is expected to reach nearly 70 percent, the United Nations estimates.
Some governments, heeding public protests, have tried to quiet the clamour of urbanisation by adopting night-time flight bans, incentivising quieter technologies and issuing fines for noise complaints. Individuals can help themselves by ensuring that bedrooms are as quiet as possible by retrofitting windows or hanging noise-reducing curtains or, if they can afford it, moving to quieter neighbourhoods.
Cheaper solutions, Basner says, may be wearing earplugs at night or moving bedrooms to a quieter part of the house. He believes people should take such steps even if they don’t find themselves especially fazed by noise.
- A Knowable Magazine report