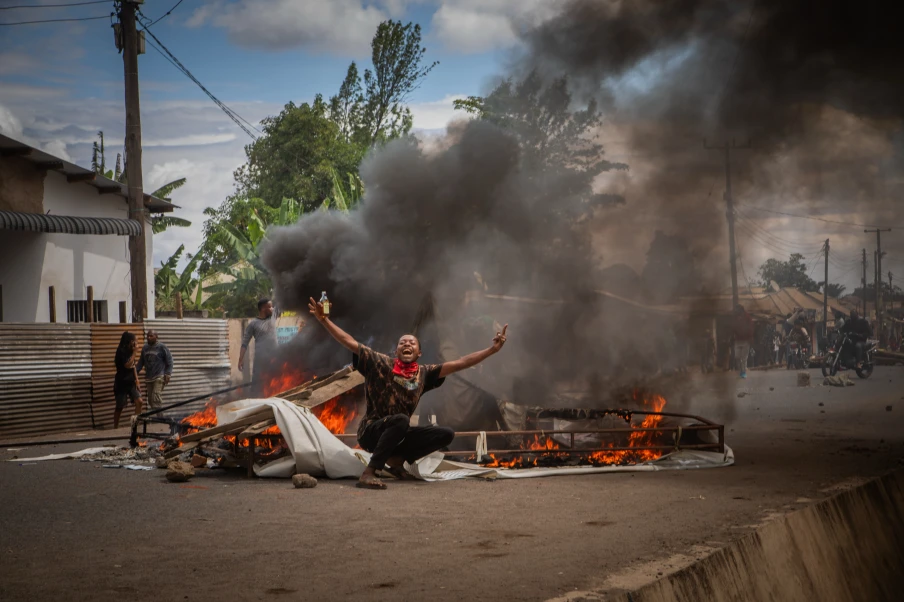Making of a Swahili Nation: How bloody repression in Tanzania, Uganda and Kenya gave birth to quest for new dispensation
Tanzania is the result of the 1964 merger of two former states – Tanganyika, the mainland territory, and Zanzibar, the coastal archipelago. The merger followed Tanganyika’s independence from Britain in 1961 and the Zanzibar Revolution in January 1964 that led to a new government that sought unification with Tanganyika.
What to know about Tanzania president’s ‘white collar hit squad’ after bloody chaos
President Samia Suluhu Hassan, who took office in 2021 after the death of her predecessor, took more than 97 per cent of the vote, according to an official tally. Her main rivals, Tundu Lissu of Chadema and Luhaga Mpina of ACT-Wazalendo, were barred from running.
Tanzanian’s Idi Amin Dada incarnate: Curse of yellow flags and why East Africans are calling President Suluhu Hassan ‘Idi Amin Mama’
Notably, the inauguration of President Samia Suluhu Hassan was done without the participation of the people she claims gave him 97 per cent of the vote. The election body has been careful not reveal voter turnout that can help shed light on Suluhu Hassan’s sudden popularity. The unprecedented feat is “bettered” on by Paul Kagame of Rwanda who in the last presidential election garnered 99.1 per cent of the vote.
How election thievery became democracy: Paradox of Africa with world’s youngest population is ruled by oldest presidents
The trend points to deeper structural problems with Africa’s underlying political environment, said Jeffrey Smith, executive director of democracy-focused Vanguard Africa non-profit. He said all three countries feature incumbents leveraging state resources to stay in power, partisan security forces as well as flawed legal processes.
Coup in the offing? Tanzania sinks further into abyss as military appears sympathetic to protesters
A similar situation to what is happening in Tanzania is also currently unfolding in Cameroon where 92-yar old Paul Biya – in power since 1982 – was early this week declared winner, sparking protests that have since received the support of the military. Like President Suluhi Hassan, President Biya – who spends more than 80 per cent of his time in France – had used the courts, police and electoral commission to arbitrarily lock out opponents.
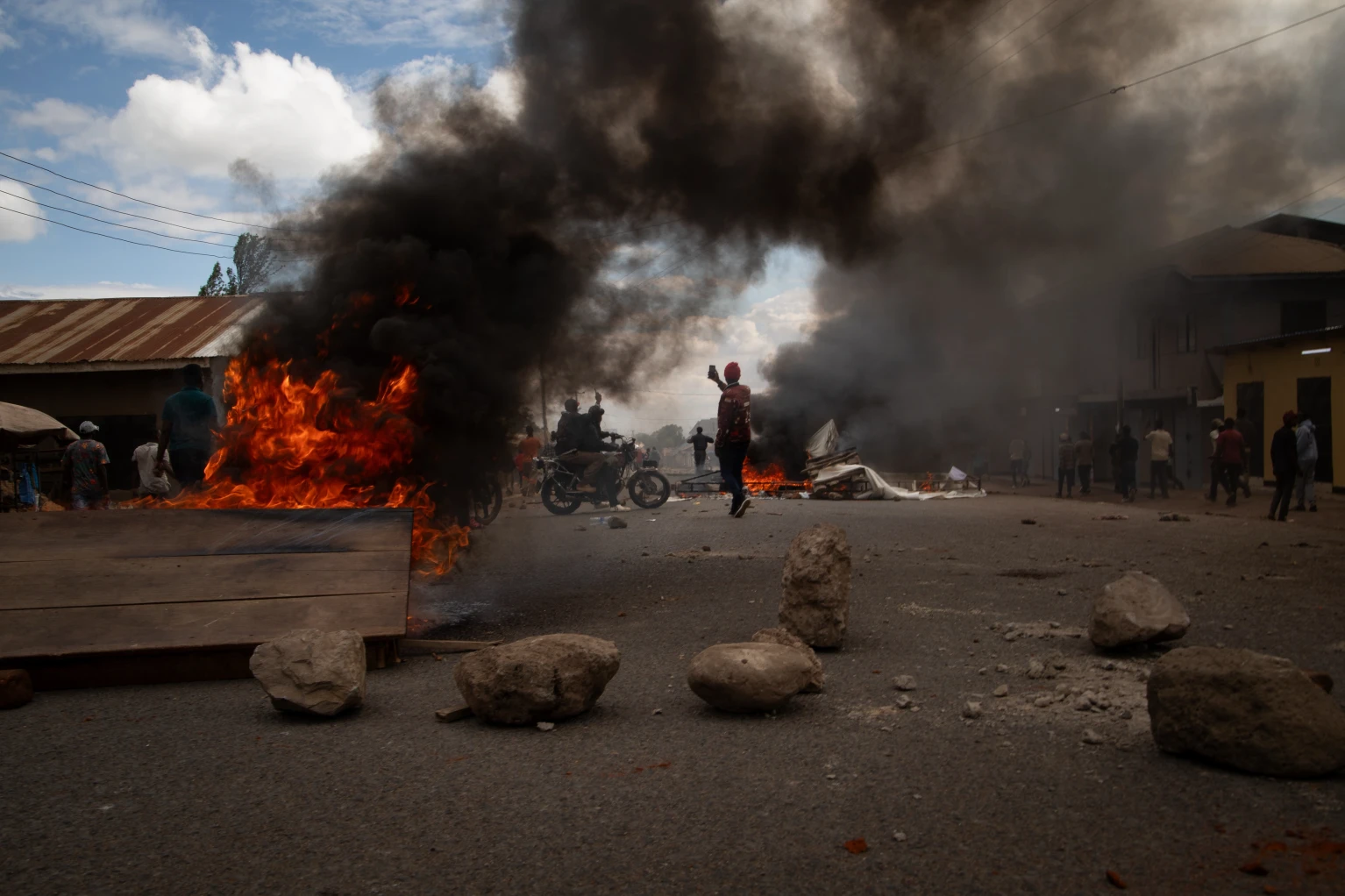
New violence erupts in Tanzania as voters say they transitioned from ‘cows to active citizens’, state directs civil servants to ‘work from home’
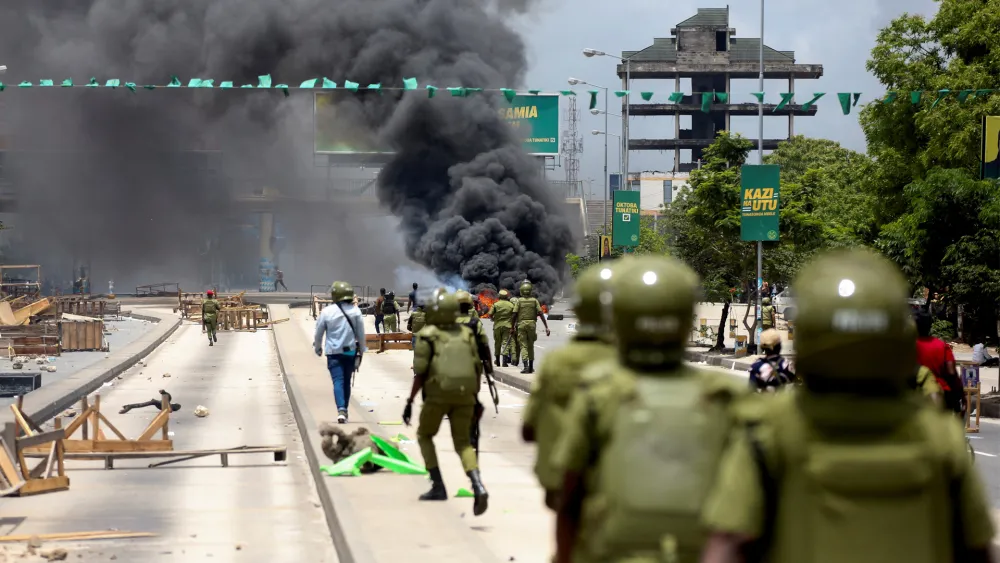
Hundreds protested on Wednesday in Tanzania’s largest city, tearing down banners of President Samia Suluhu Hassan and burning a police station, as the East African country went to the polls in elections where the main challengers have either been jailed or barred from standing.
Election violence: Tanzania police declare curfew in capital, Dar es Salaam, to suppress ‘Suluhu coronation’ protests
Chadema had called for protests during the election, which it said amounted to a “coronation” of Hassan, who came to power in 2021 after her predecessor died in office. The party was disqualified in April after it refused to sign a code of conduct, and its leader Tundu Lissu was charged with treason.
- 1
- 2