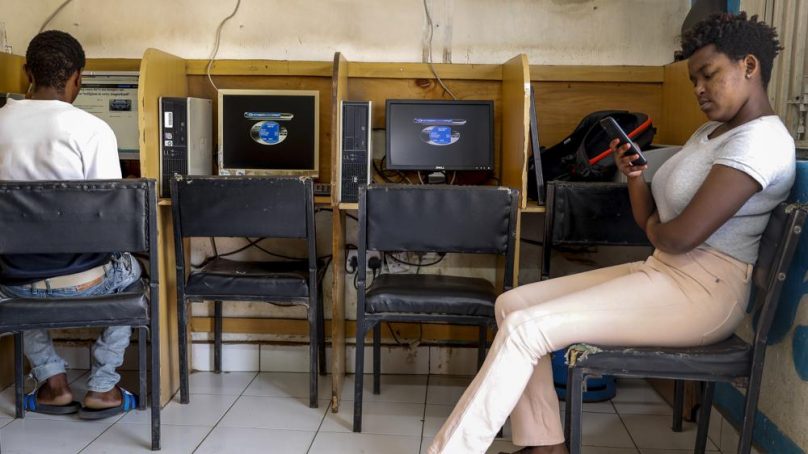
A new study has found that Facebook has failed to catch Islamic State group and al-Shabab extremist content in posts aimed at East Africa as the region remains under threat from violent attacks as Kenya prepares to vote in a closely contested national election.
An Associated Press series last year, drawing on leaked documents shared by a Facebook whistleblower, showed how the platform repeatedly failed to act on sensitive content including hate speech in many places around the world.
The new and unrelated two-year study by the Institute for Strategic Dialogue found Facebook posts that openly supported IS or the Somalia-based al-Shabab — even ones carrying al-Shabab branding and calling for violence in languages including Swahili, Somali and Arabic — were allowed to be widely shared.
The report expresses particular concern with narratives linked to the extremist groups that accuse Kenyan government officials and politicians of being enemies of Muslims, who make up a significant part of the East African nation’s population. The report notes that “xenophobia toward Somali communities in Kenya has long been rife.”
The al-Qaida-linked al-Shabab has been described as the deadliest extremist group in Africa, and it has carried out high-profile attacks in recent years in Kenya far from its base in neighboring Somalia.
The new study found no evidence of Facebook posts that planned specific attacks, but its authors and Kenyan experts warn that allowing even general calls to violence is a threat to the closely contested August presidential election. Already, concerns about hate speech around the vote, both online and off, are growing.
“They chip away at that trust in democratic institutions,” report researcher Moustafa Ayad told the AP of the extremist posts.
The Institute for Strategic Dialogue found 445 public profiles, some with duplicate accounts, sharing content linked to the two extremist groups and tagging more than 17,000 other accounts. Among the narratives shared were accusations that Kenya and the United States are enemies of Islam, and among the posted content was praise by al-Shabab’s official media arm for the killing of Kenyan soldiers.
Even when Facebook took down pages, they would quickly be reconstituted under different names, Ayad said, describing serious lapses by both artificial intelligence and human moderators.
“Why are they not acting on rampant content put up by al-Shabab?” he asked. “You’d think that after 20 years of dealing with al-Qaida, they’d have a good understanding of the language they use, the symbolism.”
He said the authors have discussed their findings with Facebook and some of the accounts have been taken down. He said the authors also plan to share the findings with Kenya’s government.
Ayad said both civil society and government bodies such as Kenya’s national counterterrorism center should be aware of the problem and encourage Facebook to do more.
Asked for comment, Facebook requested a copy of the report before its publication, which was refused.
The company then responded with an emailed statement.
“We’ve already removed a number of these pages and profiles and will continue to investigate once we have access to the full findings,” Facebook wrote Tuesday, not giving any name, citing security concerns. “We don’t allow terrorist groups to use Facebook, and we remove content praising or supporting these organizations when we become aware of it. We have specialized teams — which include native Arabic, Somali and Swahili speakers — dedicated to this effort.”
Concerns about Facebook’s monitoring of content are global, say critics.
“As we have seen in India, the United States, the Philippines, Eastern Europe and elsewhere, the consequences of failing to moderate content posted by extremist groups and supporters can be deadly, and can push democracy past the brink,” the watchdog The Real Facebook Oversight Board said of the new report, adding that Kenya at the moment is a “microcosm of everything that’s wrong” with Facebook owner Meta.
“The question is, who should ask Facebook to step up and do its work?” asked Leah Kimathi, a Kenyan consultant in governance, peace and security, who suggested that government bodies, civil society and consumers all can play a role. “Facebook is a business. The least they can do is ensure that something they’re selling to us is not going to kill us.”